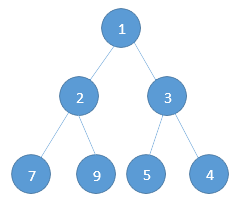
Question: Given the root pointer to a binary tree, find the number of full nodes.
Input: Sample Tree (Pointer to node 1 is given). Find the number of full nodes.
Output: Number of full nodes = 3
According to the definition, the set of all nodes with both left and right child are called as full nodes.
In the above example, we have the nodes – 1. 2, 3 as full nodes.
We can perform a level order traversal and count the number of nodes, who have their right child and left child as not null. Return the count in the end.
#include<stdio.h>
#include<malloc.h>
struct binaryTreeNode{
int data;
struct binaryTreeNode * left;
struct binaryTreeNode * right;
};
int numberOfFullNodes(struct binaryTreeNode * root)
{
// Level order traversal
struct binaryTreeNode * temp = NULL;
struct queue * Q = NULL;
// Maintain a count
int count = 0;
if(root == NULL)
return 0;
Q = enQueue(Q, root);
while(!isQueueEmpty(Q))
{
temp = Q -> front -> data;
// Now check if the node is a leaf node
if(temp -> left != NULL && temp -> right != NULL)
{
// This means a full node
count++;
}
Q = deQueue(Q);
if(temp -> left)
Q = enQueue(Q, temp -> left);
if(temp -> right)
Q = enQueue(Q, temp -> right);
}
// Delete the queue
free(Q);
// Now return the count
return count;
}
Time Complexity:- O(n)
Space Complexity:- O(n)
Ideone link for the sample program:- http://ideone.com/0C5baa