Delete is one of the most common operations done in any Linked List. The idea behind deleting a node is pretty simple: identify the node to be deleted and update the pointers. Just like inserting a node, we can delete a node from 3 different places. We also need to make sure that the deleted nodes are completely abandoned such that they are cleaned automatically by the language specific garbage collector.
Deleting a node from beginning:
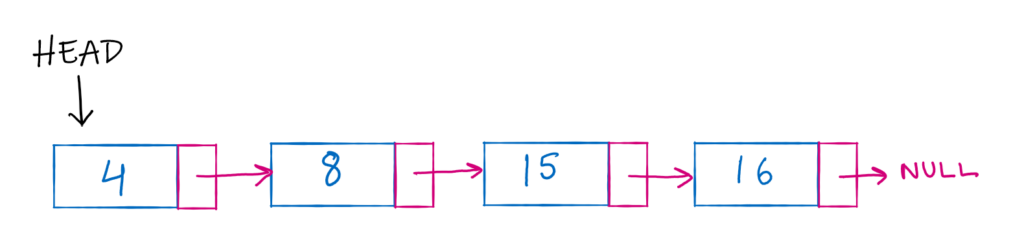
Let us consider a sample linked list with HEAD pointing at 4. We can traverse to the next node by accessing the next pointer of the first node.
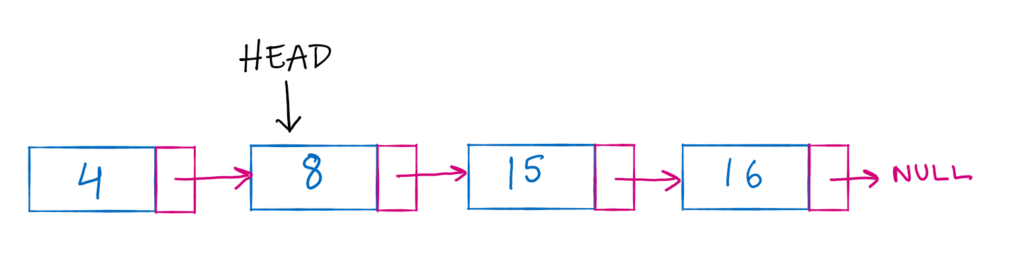
A single linked list is always identified by the head node. We can traverse all the elements if we have access to the first node. If our first node points at the second node, there is no way to reach the original node again. This way we can easily delete the node from the beginning. Just go to the next node.
Delete a node from the end:
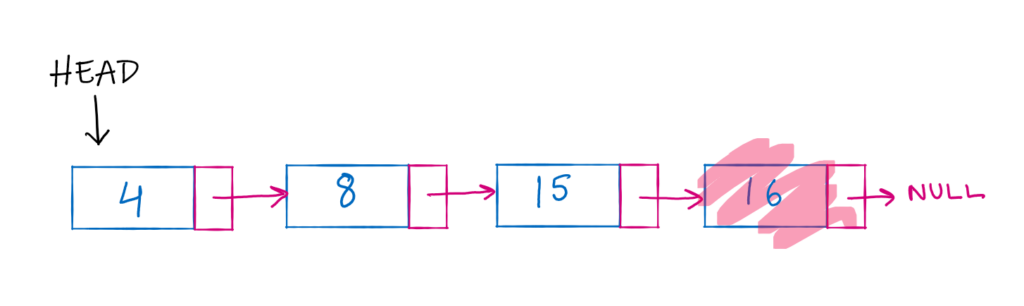
Once again, let us take a sample linked list. The last node of a single linked list is identified by the NEXT pointer pointing to NULL.
If we change the next of first node to NULL, that would remove all the nodes.
If we change the next of second node to NULL, that will just keep the first two nodes.
Hence, to delete the last node from the linked list, we can just mark the NEXT pointer of second last node to NULL.
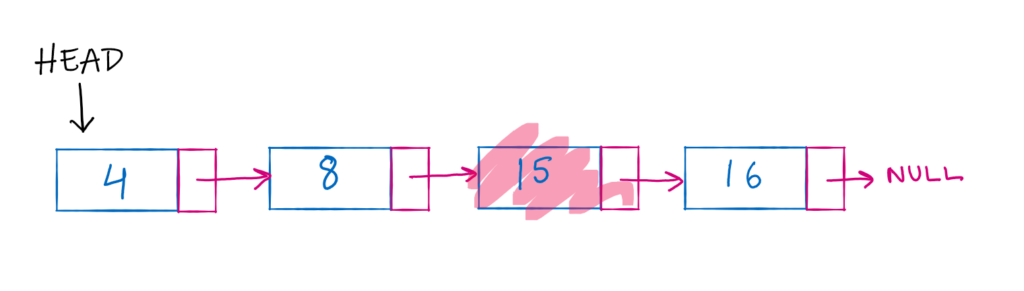
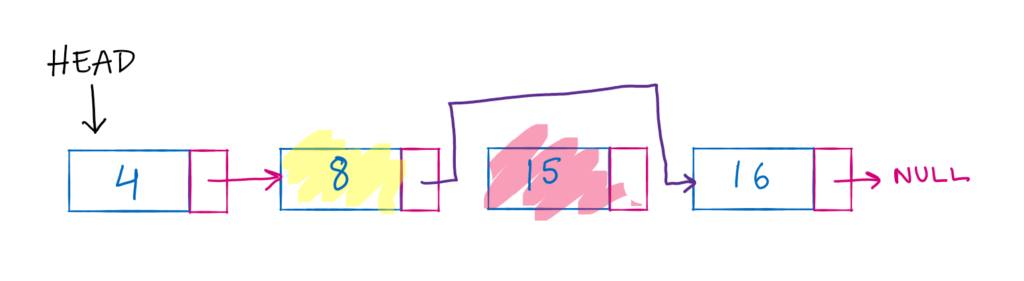
Delete a node from middle:
To remove the nodes from beginning and end, we followed two steps. Identifying the node and then updating the pointers. It is relatively easy to find the head node and last node but to find the node in middle we need to iterate over the list.
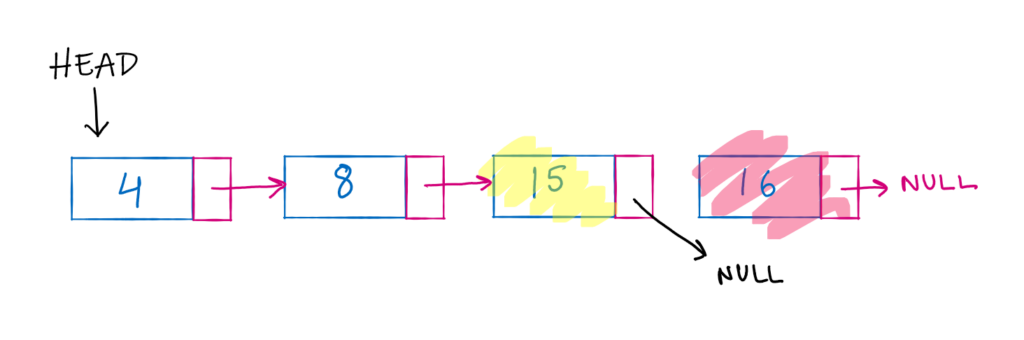
Let us take a sample list once again and we will delete the 3rd node.
We can follow the following steps:
- Choose a temp variable to iterate over the list
- Reach the 3rd position in the list
- Point the next of node previous to 3rd node to the next of 3rd node.
This will ultimately delete the node from the linked list. You need not worry about actually deleting the value from the list, as this will be cleaned up automatically by the language you are using to code.
Code:
public ListNode deleteFromBeginning(ListNode head) {
// Just move the head to the next position
head = head.next;
// Return the new head
return head;
}
public ListNode deleteAtEnd(ListNode head) {
// Move to the second last node
ListNode ptr = head;
while (ptr.next.next != null)
ptr = ptr.next;
// Point the next of second last node to null
ptr.next = null;
// Return original head
return head;
}
public ListNode deleteFromMiddle(ListNode head, int position) {
// Move to previous position of node to delete
ListNode ptr = head;
for (int i = 0; i < position - 1; i++) {
ptr = ptr.next;
}
// Get the node to delete
ListNode nodeToDelete = ptr.next;
// Get the address of node next to the node to be deleted
ListNode nextNode = nodeToDelete.next;
// Point the next of ptr to nextNode
ptr.next = nextNode;
// Return the original head
return head;
}
Code language: Java (java)The code is also available on GitHub.
Video Explanation: